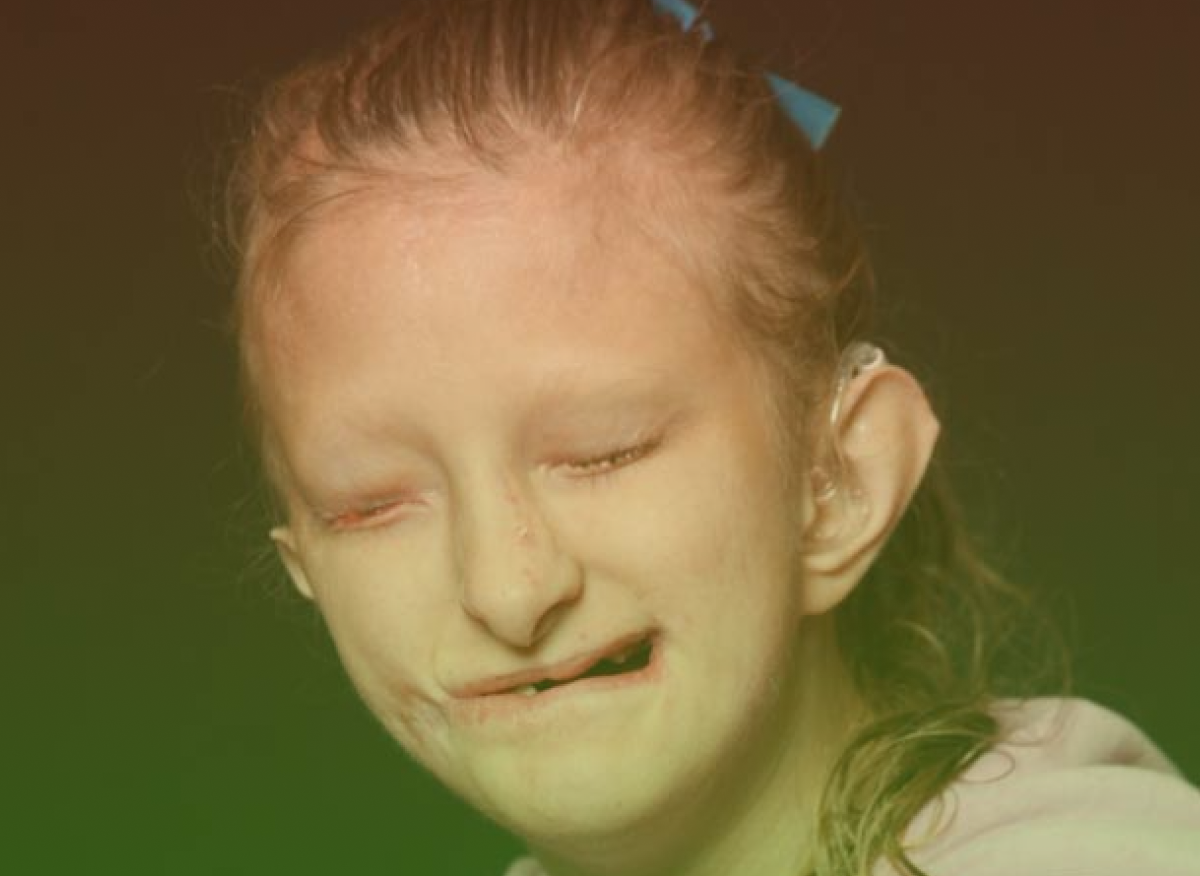
Gorlin’s disease
Gorlin’s disease, also known as cell carcinoma syndrome, affects various areas of the body and increases the risk of cancerous or non-cancerous tumours development. People with this disorder are mostly diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer. This mostly affects, back, chest or face.
The conditions usually manifest symptoms in adolescence or early adulthood. People with Gorlin’s disease have a higher risk of developing tumours in comparison to the normal population. In addition, a child born to a Gorlin’s syndrome parent has a 50-50% chance of inheriting the disease.
Gorlin Syndrome can affect people, causing them:
- Medulloblastoma- a type of brain tumour
- Fibroma development in the heart or ovaries
- Skeletal abnormalities
- Depressions in palms and feet, causing abnormality to their structure
Treatment
Symptoms
Gorlin syndrome does not always show symptoms. Still, some known symptoms are:
- A small depression in the pits of palm, feet soles
- Benign cysts of ovaries
- Benign cyst in the jawbone
Causes
The mutation of the PTCH1 gene is the major cause of Gorlin syndrome. PTCH1 is a tumour suppressor gene that helps prevent rapid cell -division. The mutation averts the production of the patched-1 gene, leading to the unnecessary production of receptors. The characteristic features of Gorlin Syndrome can be associated with chromosomal change.
- Obesity
- Gastroesophageal influx
- Family History
- Long term stomach infection
- Unhealthy toxin accumulation in the stomach.
- Stomach polyps
Diagnosis
There is no specific diagnosis for Gorlin’s symptoms. Rather, the problems caused due to it, such as cysts, tumours, etc, can be diagnosed through different diagnostic methods. Also, tracking hereditary conditions helps in the diagnosis of this condition.
Treatment
It affects various areas in different parts, causing different problems. Therefore, the treatment of the problem caused due to Gorlin’s disease, such as tumours, cysts, skin disease, etc., can be considered as a solution to Gorlin’s disease.
Once diagnosed, people with Gorlin’s disease should refrain from X-rays until an emergency because excessive exposure to X-ray may trigger cancer cell production.


